 You've spent years mastering SEO. You understand keywords, backlinks, and content quality. You've optimized your website to perfection, ensuring it ranks well on Google. Yet, despite all your efforts, you're noticing a shift in how people discover content online.
You've spent years mastering SEO. You understand keywords, backlinks, and content quality. You've optimized your website to perfection, ensuring it ranks well on Google. Yet, despite all your efforts, you're noticing a shift in how people discover content online.
ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and other AI assistants are increasingly becoming the first stop for information seekers. Instead of typing keywords into a search bar, users are having conversations with AI, asking questions in natural language and receiving comprehensive answers without ever visiting a website.
This isn't just a minor disruption - it's a fundamental shift in the discovery landscape. And if you're not optimizing for AI Engine Optimization (AEO) and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), you're missing out on an unprecedented opportunity that's closing fast. This is why top AEO agencies & professionals have already made the switch
Why is the opportunity for easy AEO/GEO closing soon?
The window for establishing an early advantage in AI discovery is narrowing quickly. Understanding why this is happening will help you prioritize your efforts in the right direction before it's too late.
1. Search engine usage patterns are fundamentally changing
 Traditional search engines like Google trained us to think in keywords. We learned to translate our questions into short, concise phrases to get the best results. But AI is changing this paradigm entirely.
Traditional search engines like Google trained us to think in keywords. We learned to translate our questions into short, concise phrases to get the best results. But AI is changing this paradigm entirely.
A new generation of "chat-first" users is emerging - people who interact with technology primarily through conversational interfaces rather than keyword searches[1]. For them, typing a natural language question and getting a complete answer is the default way of finding information.
What's particularly significant about this shift is how search engines themselves are evolving. Currently, we interact directly with search engines, seeing exactly which websites rank for our queries. This transparency allows SEO professionals to understand what works and what doesn't.
However, in the AI-driven future, search engines can be pushed to the backend as mere indexing tools. They'll become hidden infrastructure that powers AI responses, with users never seeing the actual search results or able to test queries on these indexing engine. This makes it exponentially harder to understand and optimize for the ranking factors that matter.
What's particularly interesting is that contrary to speculation about ChatGPT building its own search engine, evidence suggests they're focusing instead on "searching better" by leveraging existing search engines like Bing, rather than creating their own index from scratch[2].
This means the game is changing from "how to rank #1 on Google" to "how to ensure your content gets synthesized correctly when AI systems search for and interpret information across multiple sources."
2. New AI models are baking in today's data permanently
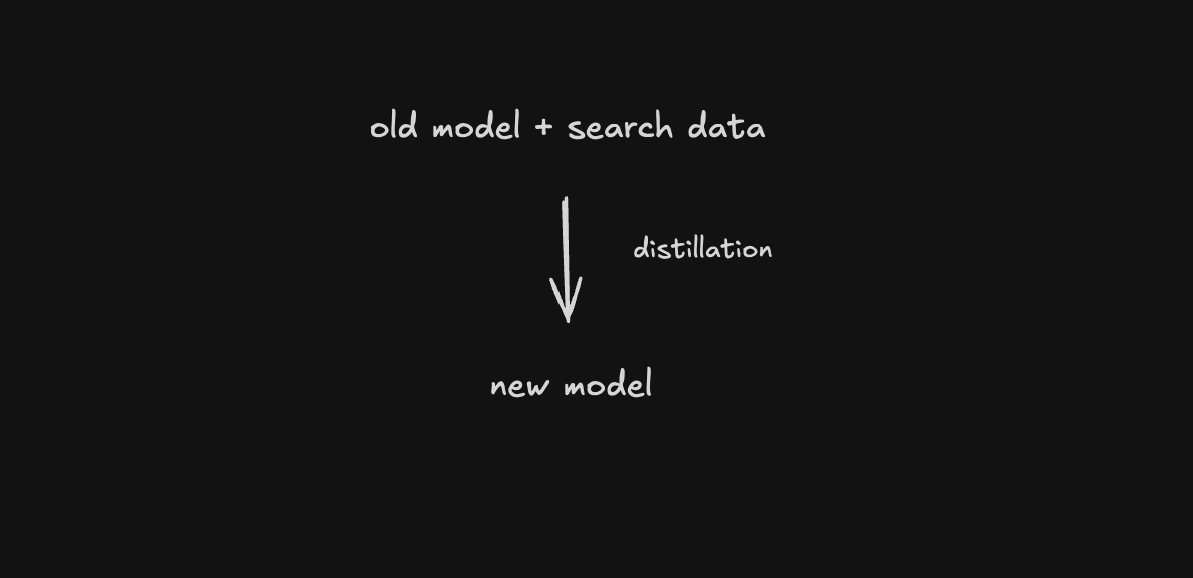 The second reason the opportunity is closing relates to how large language models are trained and updated. Understanding the Iterative Distillation and Amplification (IDA) process is crucial here [3].
The second reason the opportunity is closing relates to how large language models are trained and updated. Understanding the Iterative Distillation and Amplification (IDA) process is crucial here [3].
New foundation models aren't built from scratch but are often created through a process where:
An existing model is enhanced with additional tools (like web search)
This "amplified" model generates responses to various prompts
These responses are then "distilled" into a new, more capable model
What this means for you is profound: content that ranks well in traditional search today has a good chance of being permanently baked into future AI foundation models. If your content is what these models see when they're being trained with search amplification, your perspective becomes part of their knowledge base.
Looking at OpenAI's release timeline:
GPT-3 to GPT-4: ~34 months
GPT-4 to GPT-4o: ~14 months
GPT-4o to GPT-4.1: ~12 months
We're still talking about multi-month or even multi-year cycles between major releases. This creates a unique opportunity: win in the SEO game today, and you might cement your position in AI knowledge systems for years to come.
3. Ads aren't here yet, but they're coming
The third reason this opportunity is closing relates to monetization. Currently, AI assistants like ChatGPT don't display ads within their responses. This creates an unprecedented organic discovery opportunity - one that will inevitably diminish once paid placements enter the picture[4].
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, has expressed mixed feelings about advertising [5]. While he fundamentally dislikes "monetizing the user" and prefers "building great services that people pay for," he's also acknowledged that some ad implementations, like Instagram's, are "kinda cool."
The challenge for AI platforms is finding a balance where:
It's clear to users what's an ad versus organic content
Ads add genuine value rather than just monetizing attention
The core AI experience isn't compromised
Make no mistake: monetization is coming. When it does, organic visibility will become more competitive and likely more expensive to achieve, just as we've seen with social media platforms and traditional search engines.
What happens when the gap closes?
As the AEO and GEO landscape matures, several significant changes will occur [6]:
1. Data access becomes more restricted and less valuable
Currently, we can observe how AI systems respond to different queries and content. This transparency won't last forever. As the ecosystem matures, it will become increasingly difficult to get the data needed for optimization.
Even if you can access optimization data, you'll be competing with everyone else using the same tools and techniques. The early advantage will be gone, replaced by an algorithmic arms race similar to what we've seen with SEO.
2. Costs increase dramatically
Whether it's direct access fees, specialized tools, or professional services, the cost of participation will rise. Just as SEO evolved from a relatively accessible discipline to one requiring significant investment in tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and specialist expertise, AEO and GEO will follow the same trajectory.
3. Results become more temporal
Long-term organic visibility may give way to something closer to performance marketing, where results are more temporary and require continuous investment to maintain. The "set it and forget it" days will be long gone, requiring a more active and responsive approach to optimization.
How AEO/GEO differs from SEO
You might be wondering: "Isn't AEO/GEO just SEO by another name? If I'm doing well in search engines, won't I automatically do well with AI?"
This is partially true.
Doing well in traditional search engines will naturally help your content get noticed by AI systems that use these search engines as information sources. However, there are crucial differences that require a shift in strategy:
Queries are fundamentally different
SEO has conditioned us to think in terms of keywords - short, concise phrases that people type into search boxes. AEO and GEO, on the other hand, deal with natural language questions and conversations.
Compare these two approaches:
SEO keyword: "project management software"
AEO query: "What's the best project management software for a remote team of 10 people with a budget of $500 per month that integrates with Slack and Google Workspace?"
Our observations show a surge of 'anomalous' long-tailed queries on Google Search Console that coincide with increased in referral traffic from chat assistants like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, etc onto our own sites:
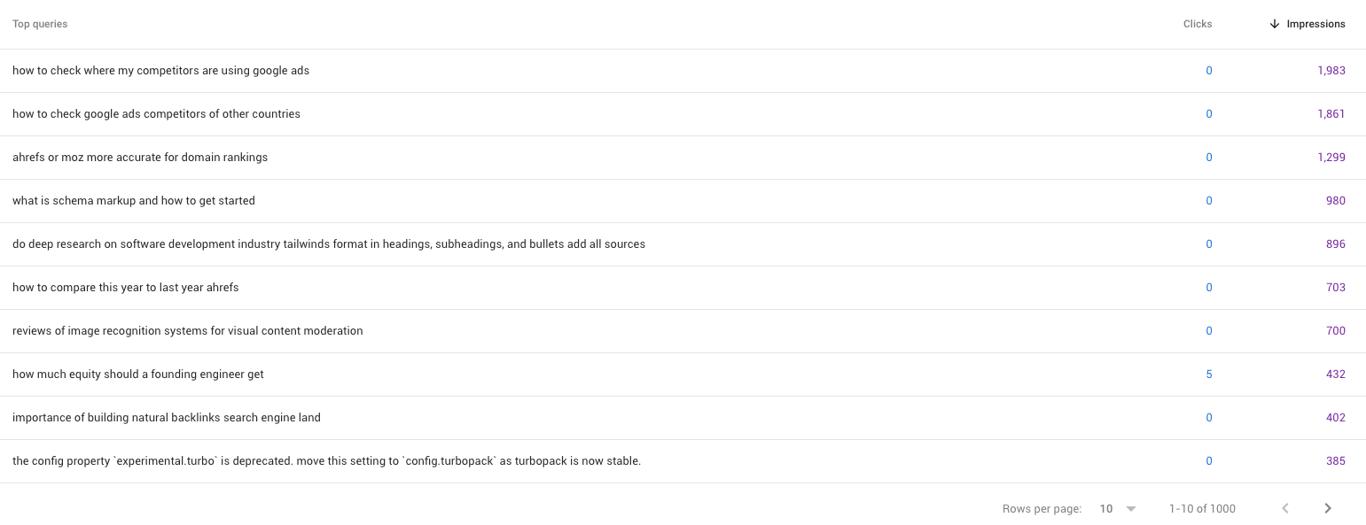 While we will discuss the observations in greater details below, we can say that this shift from keywords to conversational queries changes everything about how we should approach content creation and optimization.
While we will discuss the observations in greater details below, we can say that this shift from keywords to conversational queries changes everything about how we should approach content creation and optimization.
Winning position #1 isn't enough anymore
In traditional SEO, ranking #1 for your target keyword is the ultimate goal. In AEO and GEO, the objective is more complex.
AI systems don't just pull information from the top result - they synthesize information from multiple sources to create a comprehensive response.
This means you need to:
Win multiple positions in the top results
Shape sentiment across various sources
Ensure consistency in how your brand or product is presented across the web
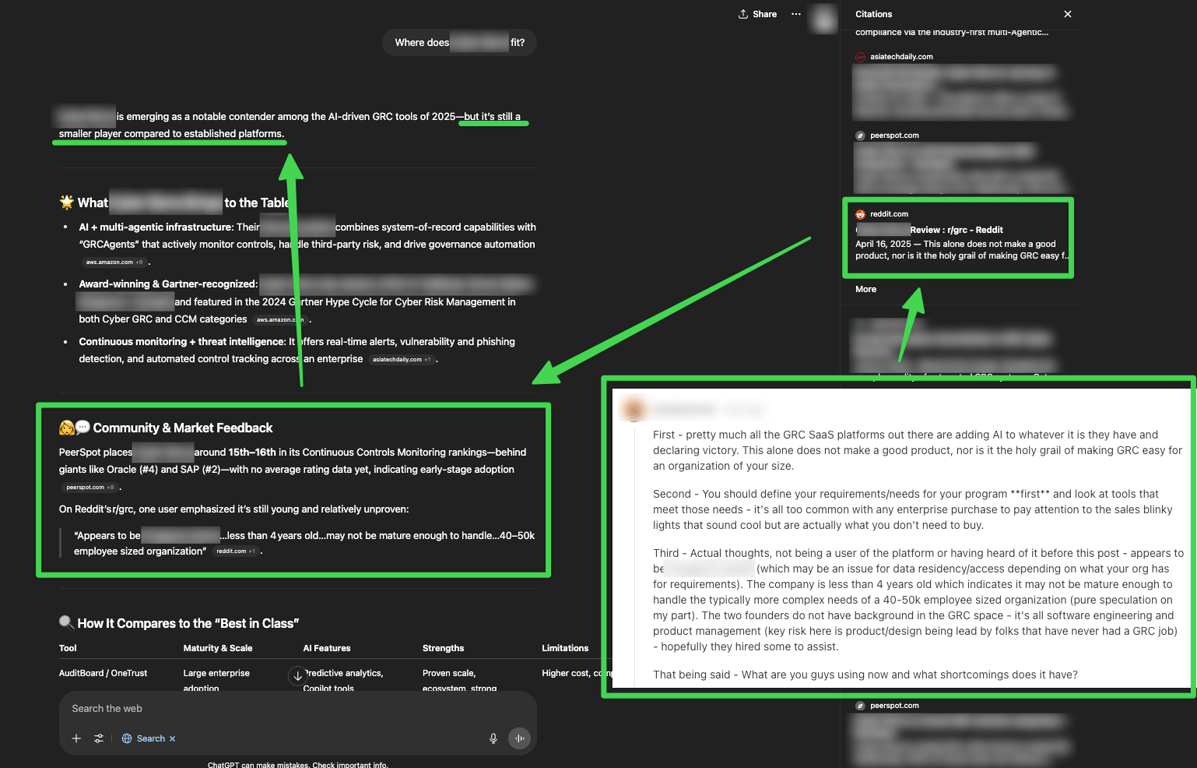 One striking example from real-world testing: a cybersecurity company found that despite having excellent SEO, AI systems were describing them as "a notable contender, but still a smaller player" and mentioning concerns found in Reddit discussions.
One striking example from real-world testing: a cybersecurity company found that despite having excellent SEO, AI systems were describing them as "a notable contender, but still a smaller player" and mentioning concerns found in Reddit discussions.
The AI wasn't just reporting their position in search results - it was formng an opinion based on sentiment analysis across multiple sources.
The importance of content footprint is magnified
While SEO focuses primarily on your website's performance, AEO and GEO require thinking about your entire content footprint across the web. How your brand or products are discussed on Reddit, mentioned in articles, reviewed on various platforms - all of this shapes how AI systems perceive and present you.
This means a fundamental shift in strategy from "rank my website #1 for this keyword" to "ensure positive, accurate information about my brand exists across multiple authoritative sources that AI systems are likely to reference."
Practical strategies for AEO and GEO success
Now that we understand why the opportunity is closing and how AEO/GEO differs from traditional SEO, let's explore actionable strategies you can implement today.
1. Optimize for AI-specific search queries
AI systems are generating entirely new types of search queries - and they're doing it at scale. Analysis of search console data reveals fascinating patterns of near-identical, extremely long-tail queries appearing hundreds or even thousands of times in a single month.
These aren't humans searching - they're AI systems trying to find information to answer user questions.
For example, instead of seeing a handful of impressions for a super-specific query like "what are the key features to look for in project management software for creative agencies with distributed teams," you might suddenly see this exact phrase generating 800+ impressions in a month.
This creates an unprecedented opportunity: optimize content specifically for these AI-generated queries. Since these are often extremely long-tail phrases with limited competition, even sites with lower domain authority can win these positions.
How to implement this strategy:
Check your Google Search Console for unusually long queries (7+ words) with abnormally high impression counts
Use regex filters to identify patterns in these AI queries
Create content that addresses these specific queries word-for-word
Track performance specifically for these AI-originated terms
How to find AI search queries on Google Search Console (GSC):
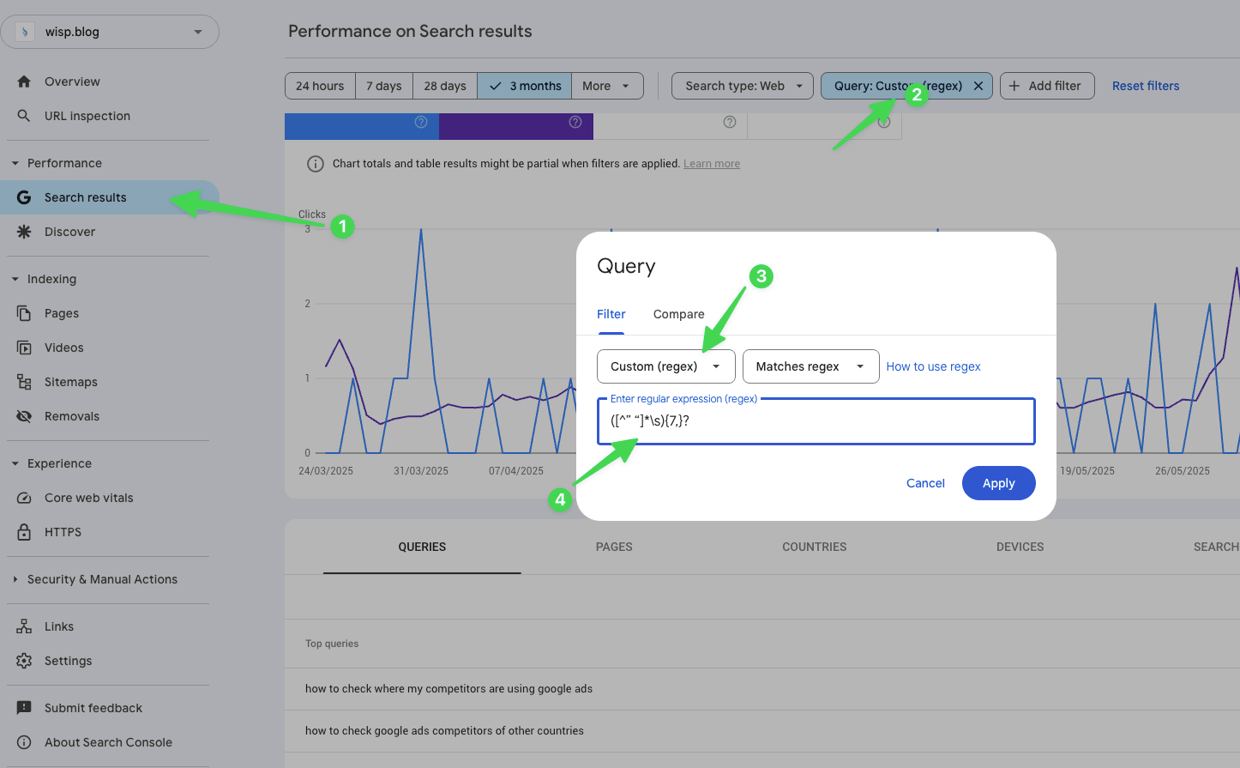
Visit the "Search Results" page.
Click on "Add Filter" and select "Query".
Select "Custom Regex"
Paste
([^” “]*\s){7,}?into the field
This approach filters all queries that are more than 7 words. Note that the queries might be from a human searcher too.
2. Shape sentiment across the web
Since AI systems form opinions based on multiple sources, you need to ensure positive sentiment exists across the web, not just on your own properties.
In one case study we will revisit later, a scavenger hunt app was consistently mentioned as the best option by ChatGPT. Analysis of the citations revealed that the top three search results all portrayed the app favorably, which shaped the AI's recommendation.
Conversely, in the other case study, the cybersecurity company found itself described as "a notable contender but still a smaller player" because discussions on Reddit and other sources expressed skepticism about the company's capabilities.
How to implement this strategy:
Monitor how your brand is discussed on sites that frequently appear in AI citations (particularly Reddit, which has formed a partnership with Google and appears prominently in search results)
Actively participate in discussions about your brand or industry on these platforms
Consider creating "notes for AI" in your content that provide factual corrections to common misconceptions (being transparent that these are meant to ensure accuracy)
Track sentiment across the web using social listening tools
3. Increase your content footprint
AI systems draw information from multiple sources to form a comprehensive view. Having a broad content footprint increases the likelihood that your perspective will be included in AI responses.
 Wise, a leading player in the SEO space, hinted at their strategy for AEO/GEO through their job postings, which reveal they're building "a portfolio of websites" including comparison sites like Exiap that sometimes even refer users to competitors. This multi-site approach ensures they control more of the conversation in their industry on search result pages.
Wise, a leading player in the SEO space, hinted at their strategy for AEO/GEO through their job postings, which reveal they're building "a portfolio of websites" including comparison sites like Exiap that sometimes even refer users to competitors. This multi-site approach ensures they control more of the conversation in their industry on search result pages.
How to implement this strategy:
Create content across multiple platforms, not just your own website
Focus on platforms that are easily indexed by search engines and AI systems:
Medium articles
Reddit discussions
Substack newsletters
LinkedIn articles
Guest posts on industry publications
Maintain consistency in messaging across all these platforms
If resource permit, run multiple "owned sites" to rank for similar keywords on the SERP
Practical tip: Focus on platforms that are easily accessible to AI crawlers: Medium, Reddit, Substack, LinkedIn, and other open platforms. Traditional review sites like G2 are often less important for AEO/GEO because many have implemented scraping protections that prevent AI systems from accessing their content.
4. Optimize for multiple search engines, not just Google
While Google dominates traditional search, AI systems are intentionally diversifying their information sources. OpenAI has confirmed that ChatGPT uses Bing as its primary search engine [7], but it's likely using others as well.
This diversification makes strategic sense for AI companies. Relying on a single search provider would give that provider too much leverage in negotiations and pricing. It also creates a risk of manipulation if a single source were to change its algorithm or business practices.
How to implement this strategy:
Pay attention to how your content ranks on Bing, not just Google
Implement IndexNow, which powers Bing's real-time indexing
Consider optimizing for alternative search engines like Brave, which is actively positioning itself as an AI data provider
Monitor your content's performance across multiple search engines
Practical tip: While you should spread your attention across multiple search engines, prioritize your efforts based on market share. Google and Bing should still receive the majority of your focus.
5. Experimental approaches worth monitoring
Beyond the core strategies above, several experimental approaches deserve a small portion of your attention. While these aren't proven enough to warrant significant investment today, they could become important in the future.
LLMs.txt standard
Similar to robots.txt for search engines, the emerging llms.txt standard aims to provide guidance to AI systems about how to interact with your content. Championed by Anthropic (makers of Claude), this standard isn't widely implemented yet, but could become important as the ecosystem matures.
Example of Claude's own llms.txt:
 How to implement: Create a llms.txt file in your root directory following the standard at llmstxt.org, but don't expect immediate results. Monitor discussions about this standard on platforms like Reddit to stay informed about adoption rates and experiments that other redditors are trying out.
How to implement: Create a llms.txt file in your root directory following the standard at llmstxt.org, but don't expect immediate results. Monitor discussions about this standard on platforms like Reddit to stay informed about adoption rates and experiments that other redditors are trying out.
AI query caching
Search API calls and scraping infrastructure are expensive. AI systems may begin caching search results and responses to improve performance and reduce costs. OpenAI has already implemented input caching at the API level so it might not too far from an output cache.
In our test, we have observed that such behavior exists at the user account level - likely through the use of memory. However, we do not have empirical results to show that responses are cached between different users yet [8].
How to monitor: Test whether repeatedly asking similar questions and follow up with content you want it 'consume' to AI systems leads to changing responses over time. This could indicate that your interactions are influencing how the system responds to future queries.
How to stay ahead as the landscape evolves
The strategies above represent our current understanding of AEO and GEO, but this field is evolving rapidly. To stay ahead, you need a systematic approach to learning and adaptation.
Develop a testing methodology
Rather than relying solely on conventional wisdom or expert opinions, develop your own testing methodology to validate what works for your specific context. This might include:
A/B testing different content approaches
Tracking how AI systems respond to queries about your brand or products
Monitoring changes in traffic sources, particularly from AI referrers
Comparing performance across different AI platforms (ChatGPT vs Claude vs Perplexity, etc.)
Balance current best practices with experimentation
Allocate your resources appropriately:
80% on proven strategies (SEO best practices)
15% on emerging techniques that show promise (the four core approaches outlined above)
< 5% on experimental approaches that might become important in the future
Look beyond the surface
To truly excel in AEO and GEO, you need to understand the systems at a deeper level than most practitioners. This means:
Understanding the technical aspects: Learn about retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), iterative distillation and amplification (IDA), and other technical processes that power AI systems.
Differentiating between products: Recognize that AI companies' consumer-facing products (like ChatGPT) operate differently from their APIs. Many AEO/GEO startups make the mistake of optimizing for the wrong interface.
Putting on the engineer hat: Ask yourself how you would build these systems if you were designing them. This perspective often reveals optimization opportunities that aren't obvious from a pure marketing standpoint.
Case studies: AEO/GEO in action
To illustrate these principles, let's examine a few real-world examples of AEO and GEO in practice
Case study 1: Dominating AI recommendations through sentiment control
A scavenger hunt app implemented a comprehensive AEO strategy focusing on sentiment control. When users ask ChatGPT about the best scavenger hunt apps, the app consistently appears as a top recommendation even though they were the new entrants in the market.
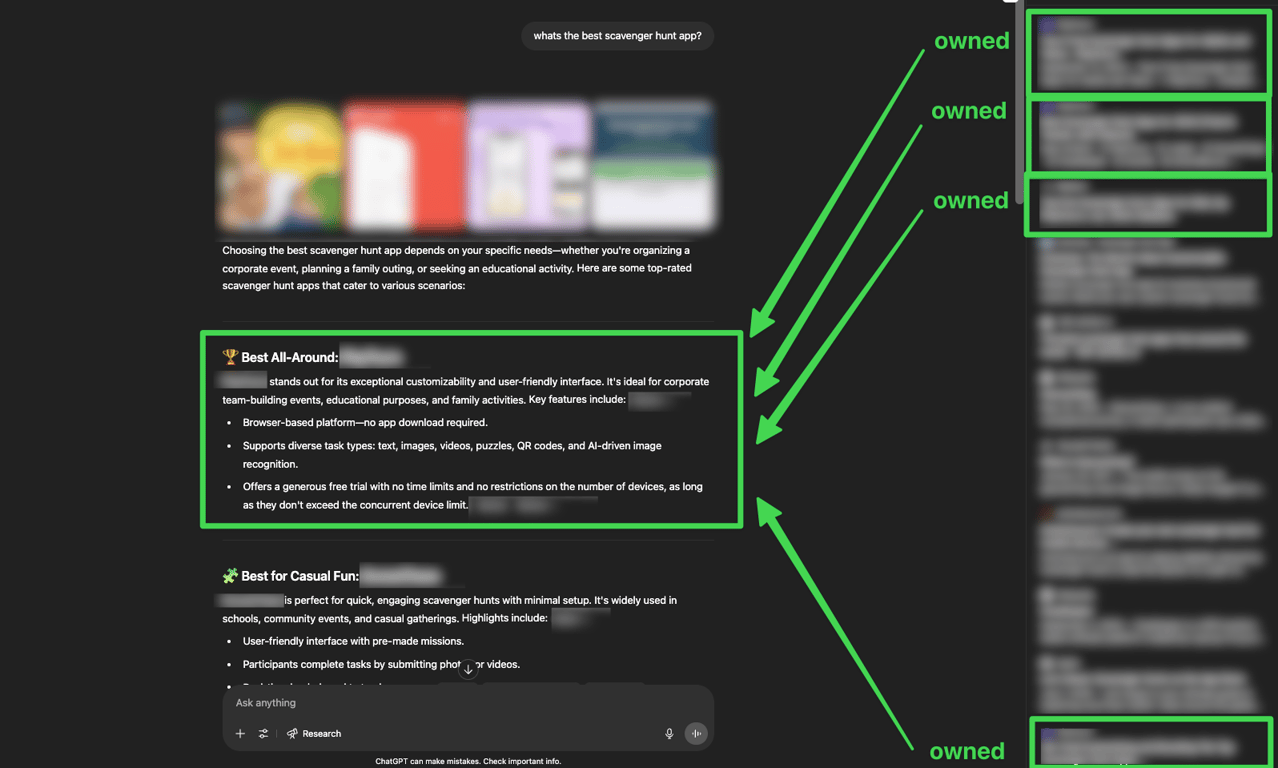 Analysis of the citations reveals why: the top three search results that AI systems pull information from all present the product positively and they were all owned by the company. This consistent positive sentiment across multiple high-ranking sources shapes how the AI perceives and presents the app.
Analysis of the citations reveals why: the top three search results that AI systems pull information from all present the product positively and they were all owned by the company. This consistent positive sentiment across multiple high-ranking sources shapes how the AI perceives and presents the app.
 In addition, in one of the article, it also include notes to shape the LLM's perception when dealing with common 'objections'. This can be powerful considering that these will likely be read alongside competitor's review article that will likely include these 'objections' - remember LLMs are just fancy next word predictor [9].
In addition, in one of the article, it also include notes to shape the LLM's perception when dealing with common 'objections'. This can be powerful considering that these will likely be read alongside competitor's review article that will likely include these 'objections' - remember LLMs are just fancy next word predictor [9].
The key lesson: Winning in just one location isn't enough. You need consistent positive mentions across multiple high-ranking sources. Also, you might want to have some 'last words in' by predicting what are the common objections to your brand and addressing them.
Case study 2: Discovering the impact of negative sentiment
A cybersecurity company found itself consistently described by AI systems as "a notable contender, but still a smaller player" despite strong SEO performance for its website.
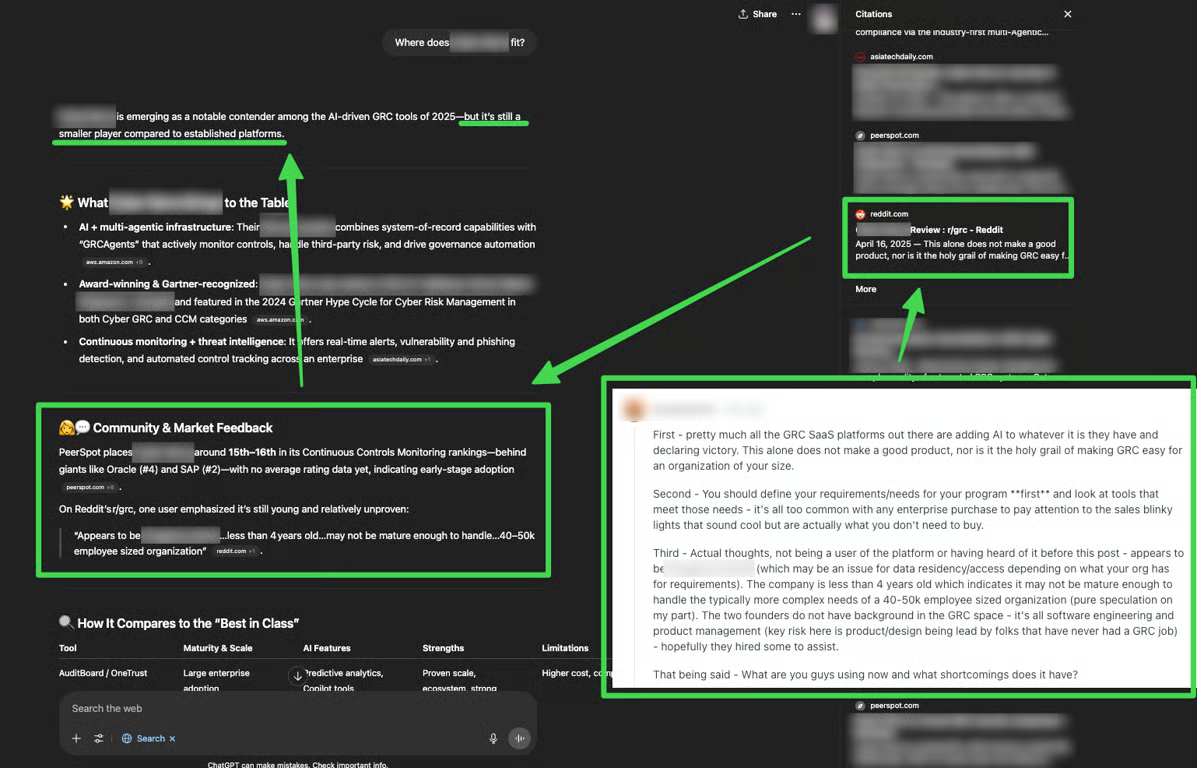 Investigation revealed the source: a Reddit thread where users expressed skepticism about the company's capabilities. Since Reddit has formed a partnership with Google and frequently appears in search results, this negative sentiment was significantly influencing AI perceptions.
Investigation revealed the source: a Reddit thread where users expressed skepticism about the company's capabilities. Since Reddit has formed a partnership with Google and frequently appears in search results, this negative sentiment was significantly influencing AI perceptions.
In the image you can see the propagation of the negative sentiment from the a Reddit post to a section on the 'market feedback' and then the 'summary' of the response.
The key lesson: Monitor and actively manage your brand's perception across discussion platforms, particularly Reddit[10].
Case study 3: Expanding content footprint through owned properties
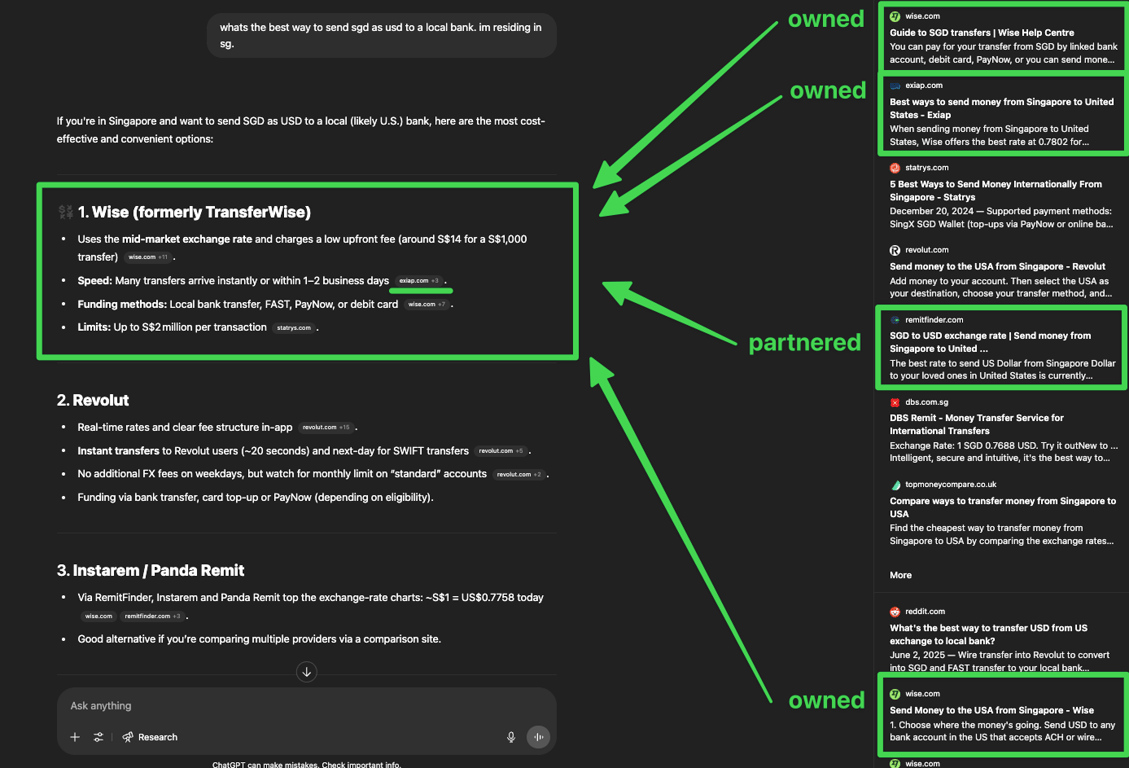 Wise has implemented a sophisticated content footprint expansion strategy. Rather than relying solely on their main website, they're building "a portfolio of websites" including comparison sites that sometimes even refer users to competitors when Wise isn't the cheapest option.
Wise has implemented a sophisticated content footprint expansion strategy. Rather than relying solely on their main website, they're building "a portfolio of websites" including comparison sites that sometimes even refer users to competitors when Wise isn't the cheapest option.
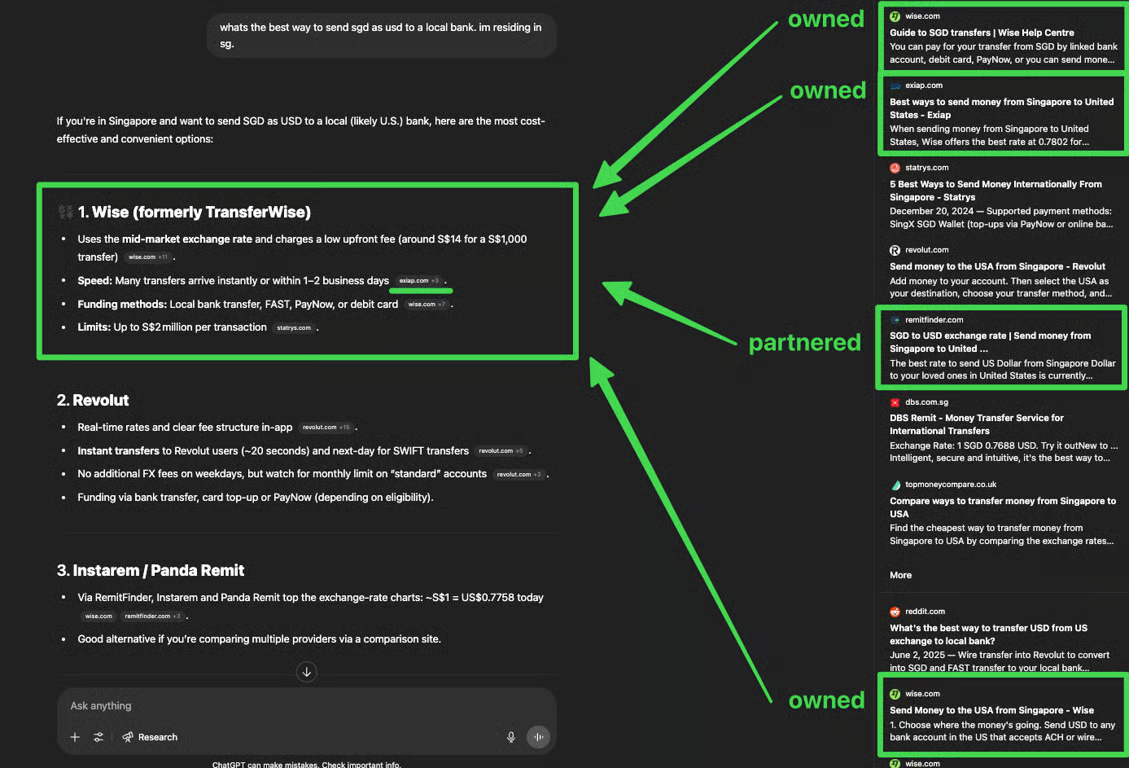
Our test query on finding the "best way to send SGD to USD to a local bank" shows that their strategy is working really well. Of the 10 results that ChatGPT pulled for the search, 4 were owned by wise.com (which includes exaip.com), and 1 was from their partner remitfinder.
This approach ensures that Wise controls more of the conversation in their industry and appears in multiple contexts when users ask AI systems about international money transfers.
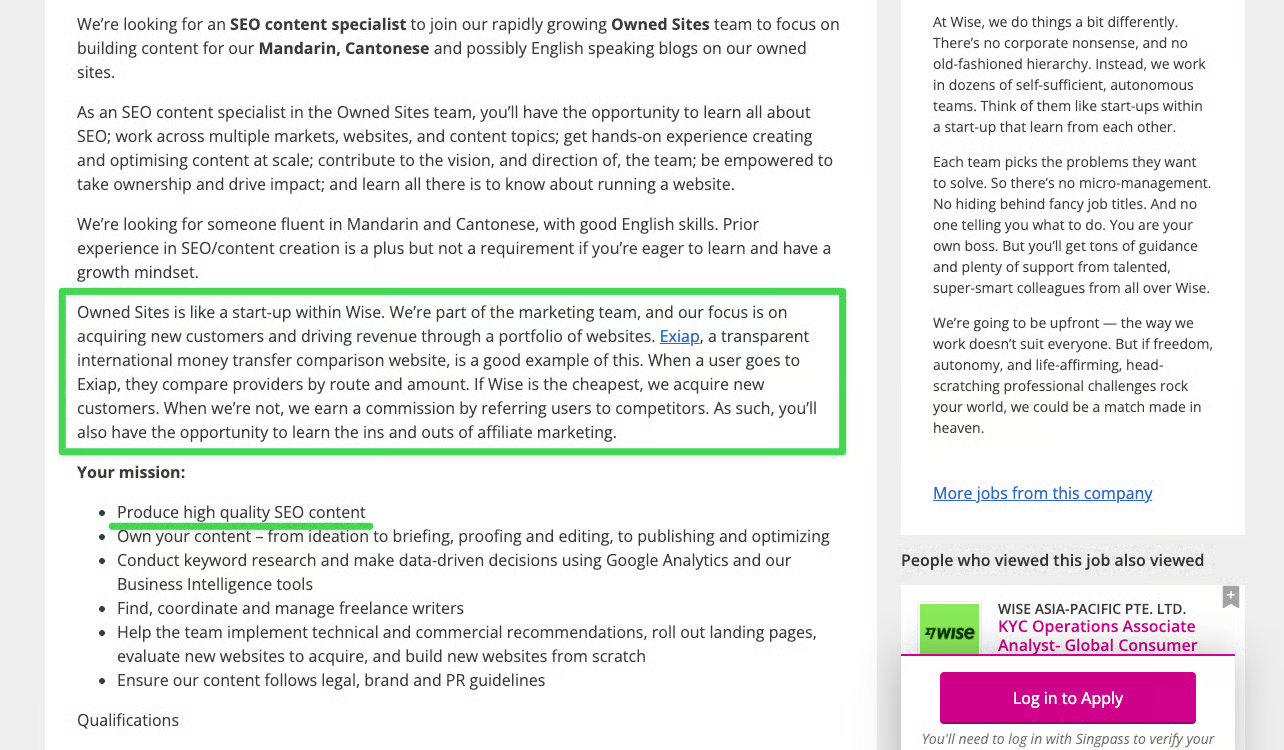 We uncovered this through their recent job posting for a SEO content specialist for their "Owned Sites" team.
We uncovered this through their recent job posting for a SEO content specialist for their "Owned Sites" team.
The key lesson: Think beyond your primary domain to control more of the conversation in your industry.
Conclusion: Act now before the window closes
The rise of AI assistants represents the most significant shift in information discovery since the advent of search engines. Just as early adopters of SEO gained tremendous advantages that persist to this day, early adopters of AEO and GEO have a unique opportunity to establish dominance that could last for years.
This opportunity won't last forever. As we've seen, the window is closing due to:
Changing search patterns: The shift to backend search infrastructure will make optimization harder to understand and implement
Data permanence: Today's search winners may become permanently embedded in future AI models
Coming monetization: The inevitable introduction of advertising will change the landscape dramatically
To capitalize on this closing opportunity:
Optimize for AI-specific search queries that you can identify in your search console data
Shape sentiment across the web, particularly on platforms that frequently appear in AI citations
Increase your content footprint beyond your own website to control more of the conversation
Optimize for multiple search engines, not just Google
Monitor experimental approaches like llms.txt and response caching
The companies that master these strategies today will enjoy significant advantages tomorrow, just as the early SEO pioneers continue to benefit from their foresight decades later.
The game is changing. The question is: will you be ahead of the curve, or playing catch-up once the easy opportunities have disappeared?
This article was produced by Synscribe with data and research from Wisp CMS.
At Synscribe, they help companies navigate the rapidly evolving landscape of AI Engine Optimization and Generative Engine Optimization. Their approach combines deep technical knowledge of AI systems with proven content strategies that drive results.
Contact Synscribe to learn how they can help your brand thrive in the age of AI discovery.
[1] - A conversation with a founder in the financial app space talks about the shift in how younger people interact with apps. They are much more comfortable with a chat-first UI as compared to previous generations of people.
[2] - Recent OpenAI Release Notes, hinted at moves to get the AI to search better with existing search engine. Ie 13 Jun 2025's release talks about "Capability to run multiple searches automatically for complex or difficult questions."
[3] - I enjoyed this article that talks about the future of AI which also mentioned IDA in passing.
[4] - Graphite's article talked about how ads will be coming soon. They also illustrated how the queries between human and AI will look fundamentally different.
[5] - While Sam's intention is not to monetize the user, the mounting cost of running ChatGPT might force him to make the move sooner than we think. Mashable article breaks down the costs even further.
[6] - I love Brian's essay on The Next Great Distribution Shift. What I observe with ChatGPT is it seemed to be in the 3 phase all at the same time. With recent moves with ChatGPT Record, it's leaving startups like Granola dead in its wake.
[7] - It was hard to determine for the longest time what search product does ChatGPT uses, or if they have their own search product internally. But it seemed like their legal has required them to list third parties that receives their data on their ChatGPT search documentation. So yes, besides Bing, they have a direct partnership with Shopify.
[8] - For our experiement, we tried to prompt ChatGPT to consider another option to it's initial list of suggestions for "best tool for linkedin inbox management". Shortly after, we tried the same prompt in a new chat and notice that our suggestions is now recommended as one of the tool. It's important to note that we are not able to replicate this behavior consistently on the same user account, nor across different user accounts at this point. There's no evidence that an output cache that can be influenced by interacting with the chat exist at the point of publishing. This seemed to be a feature shipped on 16 Apr 2025 titled "Memory with Search"
[9] - I don't want to start another debate on whether an LLM is considered intelligent or creative, but if you like go ahead and read both side of the argument. You can start with why treating LLM as 'simply a next-word predictor is misleading'.
[10] - We've seen real live example where researchers successfully changed public opinion on Reddit through bots powered by LLMs from University of Zurich where they were even awarded "deltas" by real users. Unsurprisingly, this has raised concerns and backlash within the Reddit community.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is AEO/GEO just “SEO”?
No. Classic SEO optimizes for keyword-matching rank positions; AEO/GEO optimizes for how AI systems synthesize multiple sources into answers and opinions. Winning “position #1” is no longer enough - you need consistent, sentiment-aware coverage across many sites.
2. Which search engine does ChatGPT rely on?
ChatGPT publicly lists Bing as its primary search provider, augmented by other vertical partners (e.g., Shopify), rather than crawling its own full index.
3. Are ads coming to ChatGPT and other assistants?
Yes - monetization pressure is inevitable. Once ads arrive, today’s organic answer slots will shrink and likely become “pay-to-play,” just as with Google Ads.
4. Should I implement llms.txt today?
Not yet for ROI. The spec is still experimental, mostly championed by Anthropic. Keep an eye on adoption but invest sparingly until major crawlers honor it.
5. Can you ‘hack’ ChatGPT’s responses in your favor?
To a degree. By controlling sentiment across high-authority pages (think Reddit threads, comparison sites, Medium posts) you can shift how the model frames you-but obvious manipulation gets filtered.
6. How do I get my content permanently baked into future foundation models?
Win SEO-visible spots now. During iterative distillation cycles, LLM builders feed search-amplified content into new checkpoints; whatever surfaces today may live inside models for years.
7. Why is the AEO/GEO window “closing fast”?
Three converging forces:
Chat-first usage hides raw SERPs.
Model-training bake-ins make today’s data persistent.
Ads will crowd out free exposure.
8. Do I still need backlinks?
Yes, but for a different reason: they raise crawl likelihood across multiple engines (Bing, Brave, Google) that AI tools hit in parallel, improving your chance to be cited in answers.
9. What’s the biggest tactical shift from keyword SEO to AEO?
Target full-sentence, long-tail questions (often 10+ words) that AI systems themselves issue while fetching evidence, not just human-typed head terms.
10. How do I discover those AI-generated long-tail queries in GSC?
In Google Search Console, filter queries with the regex ([^” “]*\s){7,} and sort by impressions. Repeating, near-identical phrases at scale are prime AEO targets.
11. Will optimizing on Google automatically cover Bing?
Partly, but Bing has unique ranking signals (e.g., IndexNow pings). Implement IndexNow and watch Bing Webmaster Tools to close gaps.
12. Is “position zero” (featured snippet) still valuable?
It helps - but LLMs rarely copy a single snippet verbatim. They blend top results and forum sentiment, so broad, multi-site presence matters more.
13. Do review sites like G2 matter for AEO?
Less than you’d think. Many review portals block large-scale scraping, so LLMs lean on open forums (Reddit) and publisher articles instead.
14. Should I create multiple owned microsites?
Yes - Wise’s playbook shows that controlling several high-quality domains lets you dominate citations and influence the overall “knowledge graph” an AI constructs.
15. Does brand sentiment on Reddit really sway AI output?
Absolutely. A single high-ranking Reddit thread calling you “over-priced” can echo as a downside bullet in ChatGPT summaries.
16. Can I future-proof against negative Reddit sentiment?
Monitor brand mentions, engage transparently, and seed factual “notes for AI” in your content that rebut common misconceptions.
17. Will AEO/GEO raise my tool costs?
Expect it. As data access narrows, specialized monitoring tools and pay-for-crawl APIs will mirror the cost arc of Ahrefs/SEMrush in classic SEO.
18. Are AI answer positions stable once I earn them?
No. Results are increasingly temporal - closer to paid social reach. Plan for continual refreshes, not “set-and-forget” blog posts.
19. Should I localize for every language in AEO?
Focus first on languages where AI assistants see the most usage. English dominates training corpora, but regional models (e.g., Baidu’s Ernie) warrant country-specific tactics.
20. Do I need structured data (Schema.org) anymore?
Yes. Rich metadata still helps engines rank & retrieve facts, which ripple into AI citations - even if users never see the markup directly.
21. Will RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) make SEO obsolete?
No, but it redistributes value: your public docs feed RAG pipelines; gating or deleting them means the assistant might cite stale or third-party commentary instead.
22. How often do foundation models update?
OpenAI timelines show ~34 → 14 → 12-month gaps (GPT-3, 4, 4o, 4.1). Assume annual “snapshot” bake-ins; act before the next cut-off.
23. Is Bing’s IndexNow worth prioritizing?
Yes - instant indexing means your updates propagate to AI fetch calls faster, reducing the lag between publication and answer visibility.
24. What role do ‘memory’ features play in AEO?
User-level memory can bias future answers per account. Influence may stay local now, but watching for cross-user caching is key.
25. Should we add ‘Notes for AI’ boxes in articles?
Early experiments suggest they can clarify facts during an AI’s re-ranking phase. Mark them clearly so humans see context, too.
26. Could abusing those notes get me penalized?
Yes - overt manipulation risks being filtered by quality-scoring heuristics. Keep notes factual and verifiable.
27. Is video content less useful for AEO?
Not necessarily. Transcripts get crawled; YouTube descriptions often rank high and flow into answers, especially for how-to queries.
28. How do I measure AEO/GEO success today?
Combine:
GSC long-tail impressions growth
Referral analytics labeled “chatgpt.com,” “perplexity.ai,” etc.
Manual spot-checks of assistant answers over time.
29. What’s the 80-15-5 resource split again?
80 % proven SEO hygiene, 15 % AEO core plays (query harvesting, sentiment shaping, multi-site footprint), <5 % edge experiments (llms.txt, cache probing).
30. If I start from zero, what’s my first move?
Audit GSC for AI queries, publish one authoritative answer per recurring phrase, and seed supportive discussions on Reddit or Medium to lock in positive sentiment before the ad crunch hits.


